The Needle Guide Assistant is a innovative tool designed to help users select and handle needles safely and effectively․ It provides guidance for medical and non-medical applications, ensuring proper techniques and minimizing errors․ Learn how to use needles confidently with this essential guide․
Overview of the Needle Guide Assistant
The Needle Guide Assistant is a comprehensive tool designed to assist users in selecting, using, and maintaining needles safely and effectively․ It offers detailed guidance for both medical and non-medical applications, ensuring proper techniques are followed․ Key features include size and material selection, step-by-step usage instructions, and safety precautions․ The guide also covers maintenance, storage, and disposal methods․ By following the assistant’s recommendations, users can minimize risks and achieve optimal results․ It serves as an essential resource for professionals and individuals alike, promoting confidence and precision in needle-related tasks․
Importance of Proper Needle Usage
Proper needle usage is critical for safety, accuracy, and effectiveness․ Incorrect techniques can lead to accidents, infections, or inconsistent results․ In medical settings, precise needle handling ensures patient safety and treatment efficacy․ For non-medical uses, such as crafting, proper usage prevents damage to materials and reduces injury risks․ Safe handling practices, like avoiding needle recapping and using appropriate sizes, are essential․ The Needle Guide Assistant emphasizes these principles to help users achieve their goals while minimizing risks․ Adhering to guidelines ensures optimal outcomes and protects both the user and others involved․
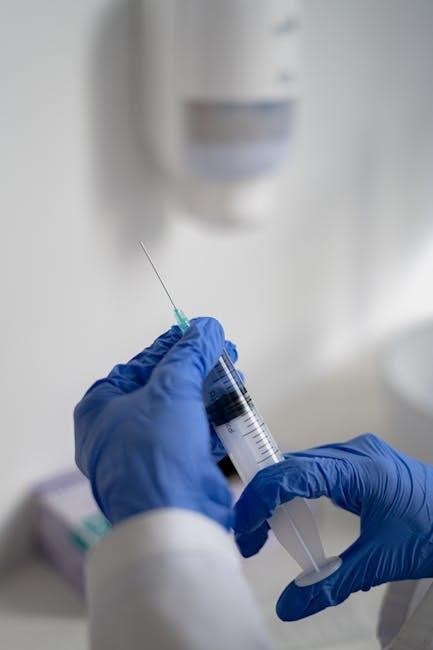
Types of Needles
Needles are categorized into medical and non-medical types․ Medical needles are used for injections, biopsies, and other procedures, requiring precision and sterility․ Non-medical needles are used for crafting, sewing, or industrial purposes, emphasizing durability and versatility․ Understanding their differences is key for safe and effective use․
Medical Needles
Medical needles are precision-engineered tools used in healthcare for various procedures, such as injections, blood sampling, and biopsies․ They come in different gauges and lengths to suit specific applications․ Hypodermic needles are commonly used for injections, while biopsy needles are designed for tissue sampling․ Proper selection and handling are crucial to ensure patient safety and accurate results․ Always follow sterile techniques and dispose of needles safely to prevent complications and infections․
Non-Medical Needles
Non-medical needles are widely used in crafting, sewing, and industrial applications․ They vary in size and material, with common types including sewing needles, knitting needles, and industrial needles․ Short circular needles are ideal for knitting socks, while large tapestry needles are perfect for heavy fabrics․ Proper selection ensures precise results․ Always store needles safely to avoid accidents and damage․ Understanding their specific uses and care tips can enhance your crafting and sewing experiences․ Learn how to choose the right needle for your project with expert guidance․
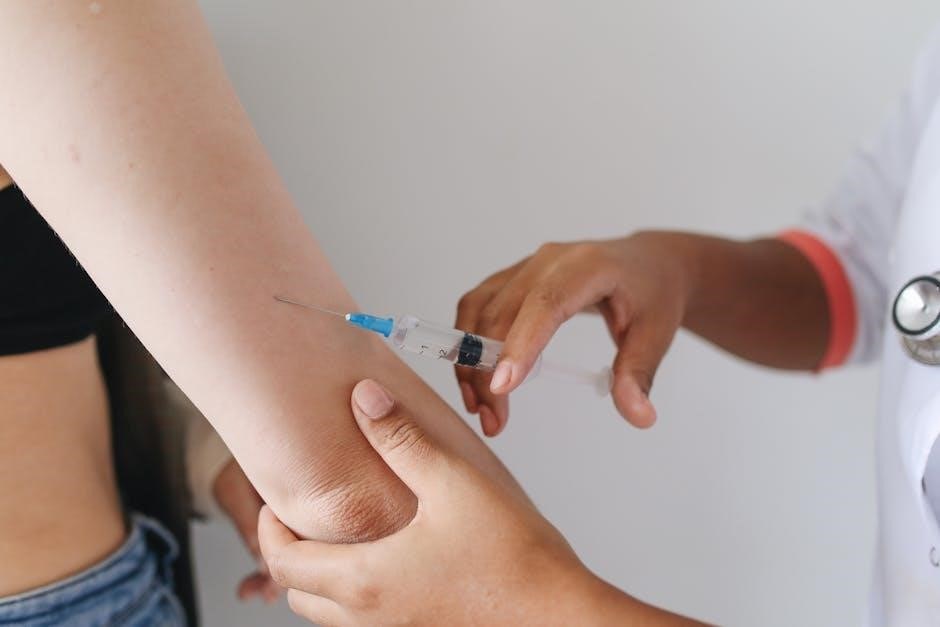
How to Choose the Right Needle
Selecting the right needle involves considering its purpose, material, and size․ Ensure it suits your task, whether for medical, crafting, or industrial use․ The Needle Guide Assistant helps you make an informed choice․
Factors to Consider
When selecting the right needle, consider its purpose, such as medical procedures, crafting, or industrial use․ Material matters, as some needles are designed for specific tasks․ Size, including length and gauge, impacts effectiveness․ Safety features, like blunt tips or ergonomic handles, reduce accidents․ Compatibility with your device or tool is crucial․ Ergonomics ensure comfort during use․ The Needle Guide Assistant helps you evaluate these factors to make the best choice for your needs․
Size and Material Selection
Choosing the right needle size involves considering its length and gauge․ Longer needles are ideal for deeper injections, while shorter ones suit shallow applications․ The gauge refers to the needle’s thickness, with higher gauges indicating thinner needles․ Material options include stainless steel for durability or disposable needles for safety․ The Needle Guide Assistant helps you match the needle size and material to your specific task, ensuring precision and safety, whether for medical, crafting, or industrial use․
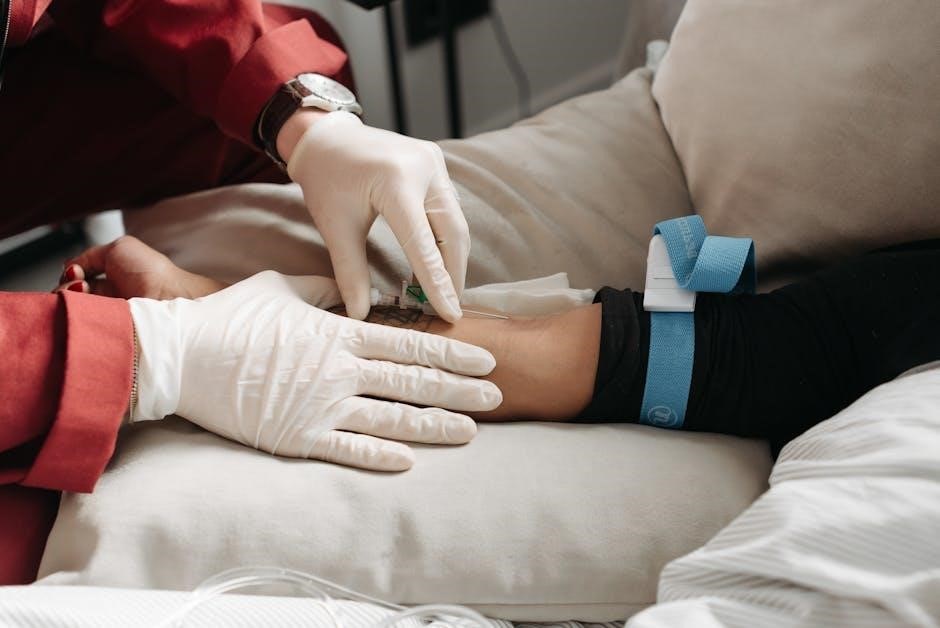
Using the Needle Guide Assistant
The Needle Guide Assistant offers real-time guidance for selecting and using needles safely․ It helps users avoid accidents and ensures proper technique for medical or non-medical tasks․
Step-by-Step Usage Guide
Using the Needle Guide Assistant involves preparing the needle, attaching it securely, and following guided instructions․ Step 1: Select the appropriate needle type․ Step 2: Attach the needle to the device․ Step 3: Set the depth and angle․ Step 4: Insert the needle as directed․ Step 5: Monitor and adjust if needed․ Always follow safety guidelines and dispose of needles properly․ This tool ensures accuracy and safety for medical and non-medical tasks, making needle usage more efficient and error-free․
Tips for Safe Handling
Always use the Needle Guide Assistant with caution․ Avoid recapping needles to prevent accidents․ Wear protective gloves and ensure a firm grip․ Store needles in a secure container when not in use․ Never share needles or reuse them․ Keep the area clean and well-lit․ Follow the guide’s instructions carefully and dispose of needles in a sharps container․ Regularly check for damage and replace worn-out needles․ Proper handling reduces risks and ensures safe, effective use of the Needle Guide Assistant for all applications․
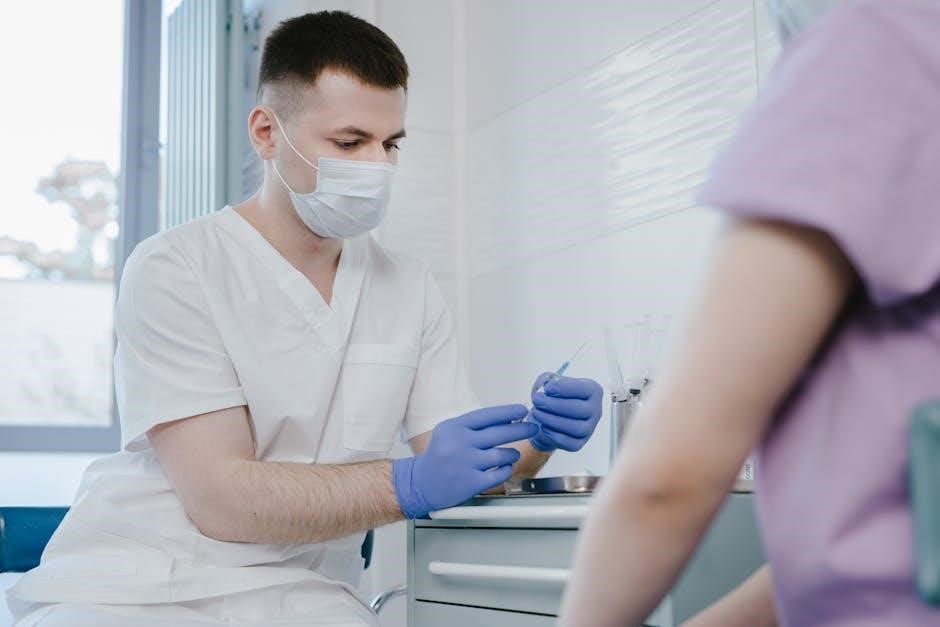
Maintenance and Care
Regularly clean and store needles properly․ Avoid exposing them to harsh chemicals․ Check for damage and replace as needed․ Proper care ensures longevity and safety․
Cleaning and Storage
Proper cleaning and storage of needles are crucial for safety and longevity․ Use alcohol wipes to clean needles before and after use․ Store them in a dry, secure container to prevent damage and contamination․ Avoid exposing needles to extreme temperatures or moisture․ Regularly inspect needles for dullness or damage․ Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for storage to ensure optimal performance and reduce the risk of accidents․ Proper maintenance helps maintain needle quality and prevents potential hazards․
When to Replace Needles
Replace needles when they show signs of dullness, rust, or damage․ Dull needles can cause discomfort or inaccurate results․ If a needle is bent or has visible wear, it should be replaced immediately․ Medical needles should be discarded after a single use to prevent contamination․ Non-medical needles, like those used in crafting, should be replaced when they become difficult to handle or show signs of wear․ Regular replacement ensures safety, accuracy, and optimal performance across all applications․
Safety Precautions
Always handle needles with care to avoid accidents․ Never recap needles, as this can cause injury․ Use protective gloves and ensure proper disposal to prevent contamination and hazards․
Handling Needles Safely
Always handle needles with extreme care to prevent accidents․ Avoid recapping needles, as this is a common cause of injuries․ Use protective gloves when handling needles to reduce the risk of punctures․ Ensure needles are stored in a secure, puncture-proof container when not in use․ Never leave needles exposed or within reach of children․ Follow proper disposal methods to prevent contamination and hazards․ Always use a needle guide or assistant to stabilize the needle during procedures․ Proper handling techniques can significantly reduce the risk of needlestick injuries and ensure a safer environment for everyone involved․
Proper Disposal Methods
Proper disposal of needles is crucial to prevent accidents and contamination․ Use puncture-proof containers specifically designed for sharps disposal․ Never dispose of needles in regular trash or recycling․ Always follow local regulations for needle disposal․ Participating in needle exchange programs or using designated drop-off locations is highly recommended․ Ensure containers are sealed and labeled before disposal․ Avoid recapping needles, as this increases the risk of injury․ Proper disposal methods help protect healthcare workers, waste management staff, and the environment from potential hazards․
Troubleshooting Common Issues
The Needle Guide Assistant helps identify and resolve common needle-related problems․ Address issues like bent or blocked needles, improper usage, or material incompatibility with step-by-step solutions․
Addressing Common Mistakes
Common mistakes when using needles include improper selection, incorrect handling, and not following safety protocols․ The Needle Guide Assistant helps users identify these errors, providing clear solutions to minimize risks․ For instance, it alerts users about needle recapping dangers and suggests safer alternatives․ By addressing these issues, the tool ensures proper techniques and reduces accidents, promoting safe and effective needle usage across various applications․
Resolving Usage Problems
The Needle Guide Assistant is equipped to resolve common usage issues, such as incorrect needle selection or improper handling․ It provides real-time feedback and guided solutions to address problems immediately․ For example, if a user selects the wrong needle size, the assistant offers alternatives and explains why the change is necessary․ This feature ensures accurate and safe needle usage, minimizing errors and enhancing overall efficiency․ The tool is designed to adapt to various scenarios, making it a reliable resource for both beginners and experienced users․
Expert Recommendations
Experts emphasize the importance of proper needle handling and safety protocols․ They recommend using the Needle Guide Assistant for accurate selections and techniques, ensuring minimal errors and optimal results․
Best Practices from Professionals
Professionals recommend consulting healthcare experts before using needles and adhering to established safety protocols․ Always use the Needle Guide Assistant for accurate needle selection and proper techniques․ Avoid recapping needles to prevent accidents․ Ensure needles are stored correctly and disposed of safely․ Regularly update your knowledge on needle usage to maintain best practices․ Professionals also suggest practicing injections on training devices to build confidence and skill․ By following these guidelines, you can enhance safety and effectiveness in needle-related procedures․
Advanced Techniques
Advanced techniques involve mastering precise needle control and angle adjustments for specific procedures․ Professionals suggest using the Needle Guide Assistant to optimize needle size and material selection for complex tasks․ Learn to handle needles at the hub for better stability and accuracy․ Practice advanced injection methods, such as intramuscular and subcutaneous techniques, to enhance proficiency․ For intricate applications, consider using guided devices to minimize errors․ Regular practice and updating skills with the latest tools can elevate your expertise in needle usage․
The Needle Guide Assistant is an essential tool for safe and effective needle usage․ It enhances precision, reduces errors, and ensures proper techniques for all applications․ By following its guidance, users can achieve optimal results and minimize risks․ Adopt best practices today for a better tomorrow․
Final Thoughts
The Needle Guide Assistant is a vital resource for anyone working with needles, offering clear guidance to enhance safety and efficiency․ By understanding proper techniques and materials, users can minimize risks and achieve precise results․ Whether for medical procedures or crafting, this tool empowers individuals to make informed decisions․ As needle technology advances, staying informed and adopting best practices ensures better outcomes․ Embrace the Needle Guide Assistant to elevate your skills and confidence in handling needles effectively․
Future Developments
Advancements in needle technology are expected to revolutionize medical and non-medical applications․ The Needle Guide Assistant will likely integrate AI-driven recommendations, real-time feedback, and compatibility with smart devices․ Future updates may include biodegradable needle options and automated systems for safer handling․ Researchers are also exploring nanotechnology for precision medicine delivery․ As these innovations unfold, the Needle Guide Assistant will remain a cornerstone for users, adapting to new technologies and ensuring optimal safety and efficiency in needle usage across industries․