Dental surgical guides are customized tools aiding precise implant placement. Utilizing CBCT scans, they enhance accuracy, minimize complications, and improve patient outcomes in modern dentistry.
Definition and Purpose
A dental surgical guide is a customized tool, often made of acrylic resin, designed to fit over teeth or mucosal surfaces. Its primary purpose is to ensure precise placement of dental implants by guiding drills and implants to the optimal position. This enhances surgical accuracy, minimizes complications, and improves functional and aesthetic outcomes for patients.
Historical Development
Dental surgical guides evolved from early implantology techniques in the 20th century. Initially, simple radiographic templates were used, but advancements in imaging and materials led to more precise tools. The 1980s saw the introduction of stereolithographic guides, followed by computer-guided systems in the 2000s. Today, digital technologies like CBCT scans and 3D printing have revolutionized their design and accuracy, enhancing surgical outcomes.
Types of Dental Surgical Guides
Dental surgical guides are categorized into computer-guided, conventional, and hybrid types. Each offers unique advantages, catering to different clinical needs and surgical preferences for precise implant placement.
Computer-Guided Surgical Guides
Computer-guided surgical guides use CBCT scans and digital software to create highly accurate templates. They enable precise implant placement, reducing errors and enhancing surgical outcomes. These guides incorporate real-time data, improving efficiency and patient satisfaction while minimizing complications during procedures.
Conventional Surgical Guides
Conventional surgical guides are fabricated using dental impressions and 2D radiographs. Made from materials like acrylic resin, they fit over teeth or mucosa to guide implant placement. These guides are less precise than computer-guided versions but remain cost-effective for straightforward cases. They rely on manual fabrication, offering a traditional approach to implant surgery with moderate accuracy and simplicity.
Hybrid Surgical Guides
Hybrid surgical guides combine conventional methods with digital technology, offering enhanced accuracy. They utilize CBCT scans for improved precision and are fabricated using 3D printing or stereolithography. These guides blend flexibility with digital planning, making them suitable for complex cases. Hybrid guides often feature adjustable components, allowing for real-time modifications during surgery while maintaining cost-effectiveness and reducing invasiveness for optimal patient outcomes.
Design and Fabrication Process
The process involves creating detailed digital models using CBCT scans, followed by 3D printing or milling. Advanced software ensures precision, while materials like acrylic resin are commonly used.
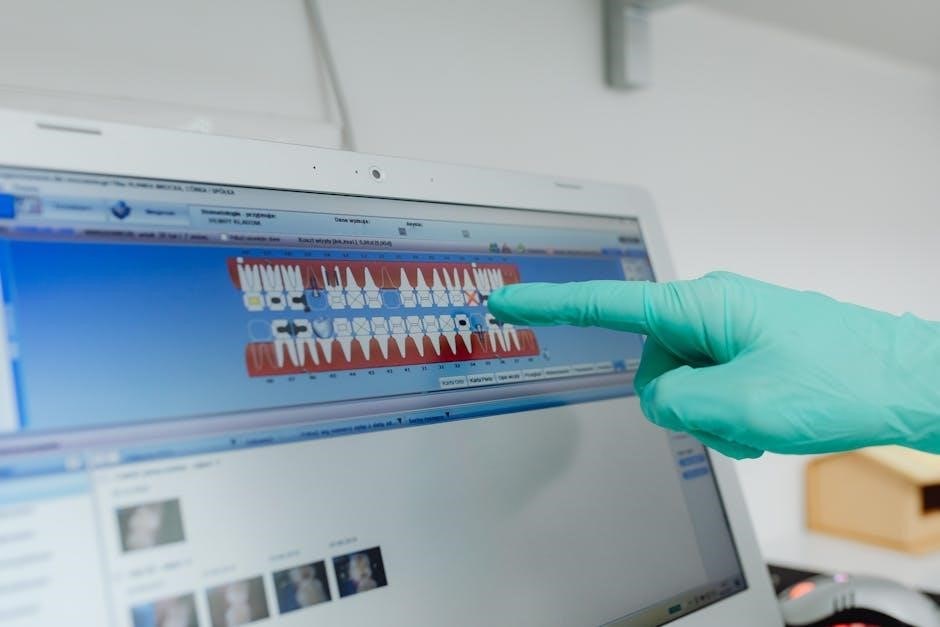
Digital Design Using CBCT Scans
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) scans provide detailed 3D imaging of the jawbone, enabling precise digital models for surgical guides. This technology allows clinicians to visualize anatomical structures accurately, ensuring optimal implant placement. Specialized software processes CBCT data to create customizable guides, minimizing surgical complications and enhancing outcomes. The digital design ensures a perfect fit and alignment with drill guides for accurate implant positioning.
Role of Software in Guide Fabrication
Software plays a pivotal role in creating precise surgical guides by processing CBCT data into detailed 3D models. It offers tools for virtual implant placement, drill guide customization, and real-time adjustments. Advanced algorithms ensure accurate alignment and fit, while compatibility with 3D printing enables rapid fabrication. This technology streamlines the design process, reducing human error and enhancing surgical precision.
Materials Used for Surgical Guides
Surgical guides are typically made from biocompatible materials like acrylic resin or specialized plastics. These materials ensure durability, precision, and sterility during procedures. Advanced 3D printing techniques often utilize reusable thermoplastics or metal for added stability. The choice of material depends on the surgical requirements, ensuring optimal fit and functionality while maintaining patient safety and comfort throughout the implant placement process.
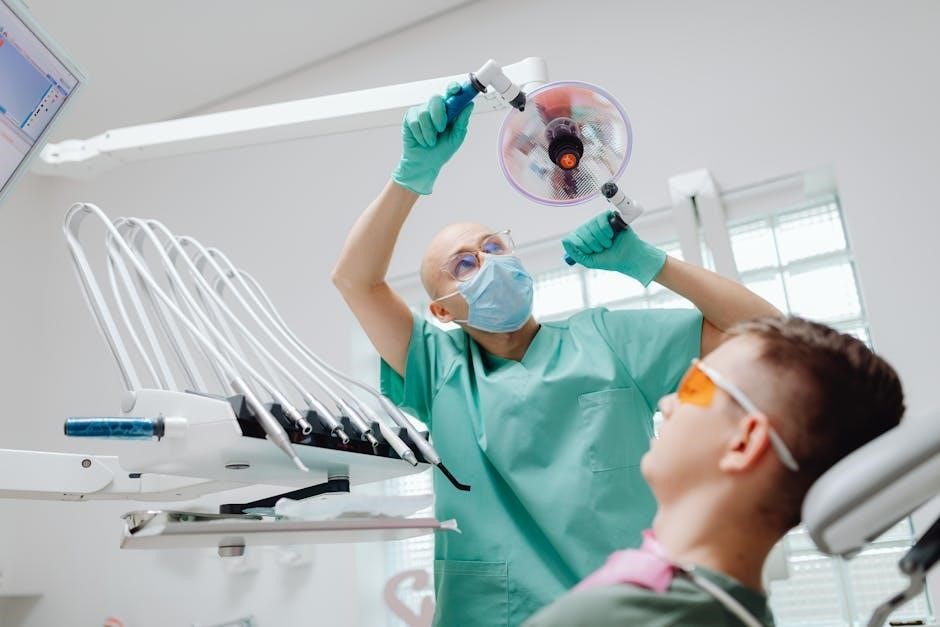

Clinical Applications
Dental surgical guides facilitate precise implant placement, bone grafting, and tissue regeneration, aiding in complex anatomical cases for predictable and successful outcomes.
Single and Full-Arch Implant Placement
Dental surgical guides are essential for precise positioning in single and full-arch implant placements. They ensure accurate alignment and minimize complications, enhancing osseointegration and aesthetics. Customized guides, often created from CBCT scans, help manage complex anatomy in full-arch cases. This approach reduces patient discomfort and recovery time, delivering functional and visually appealing results.
Bone Grafting and Augmentation
Dental surgical guides play a crucial role in bone grafting and augmentation by ensuring precise placement of grafts. They help in preoperative planning, minimizing complications, and optimizing healing. Guides created from CBCT scans provide accurate measurements, facilitating successful integration of grafts. This enhances bone density and prepares the jaw for implants, improving both functionality and aesthetic outcomes for patients.
Immediate Loading Implants

Dental surgical guides are instrumental in immediate loading implant procedures, enabling precise placement and immediate restoration. They ensure stability and proper alignment, reducing healing time and post-operative discomfort. Guides created from CBCT scans facilitate accurate positioning, allowing for immediate functional and aesthetic results. This approach streamlines the process, enhancing patient satisfaction and clinical efficiency in modern implantology practices.
Benefits and Advantages
Dental surgical guides enhance precision, reduce operative time, and improve patient comfort. They minimize complications and ensure optimal implant placement, leading to better clinical outcomes and satisfaction.
Improved Precision and Accuracy
Dental surgical guides significantly enhance precision by providing a clear roadmap for implant placement. They use CBCT scans to ensure accurate positioning, minimizing errors and complications. This reduces the need for exploratory drilling, allowing for more predictable outcomes and better preservation of surrounding tissue, ultimately leading to improved patient satisfaction and clinical success.
Reduced Surgical Time
Dental surgical guides streamline procedures by providing a pre-planned blueprint for implant placement. This minimizes exploratory drilling and adjustments during surgery, significantly shortening operation time; The clear, precise guidance allows clinicians to work efficiently, reducing anesthesia duration and patient discomfort while maintaining high standards of care and outcomes.
Enhanced Patient Experience
Dental surgical guides contribute to a more comfortable and stress-free experience for patients. By minimizing swelling, pain, and procedure duration, they reduce post-operative discomfort. The precise placement also lowers the risk of complications, fostering trust and satisfaction. Patients benefit from faster recovery times and improved aesthetic outcomes, enhancing their overall experience and confidence in the treatment process.

Advancements and Future Trends
Advancements in dental surgical guides focus on 3D printing, AI integration, and teledentistry, enhancing precision, customization, and remote planning for future dental procedures.
3D Printing in Surgical Guide Production
3D printing revolutionizes surgical guide production by enabling rapid creation of highly accurate, customized guides. Digital models from CBCT scans are transformed into physical tools, ensuring precise fits and anatomical accuracy. This method enhances production efficiency, reduces costs, and allows for intricate designs tailored to individual patient needs, making it a cornerstone of modern dental surgical guide fabrication.
AI Integration for Predictive Analytics
AI integration enhances predictive analytics in dental surgical guides by analyzing CBCT scans to predict bone density and optimal implant placement. This technology reduces surgical time and improves outcomes by providing precise, data-driven recommendations for clinicians, ensuring more accurate and efficient implant procedures tailored to individual patient anatomy.
Teledentistry and Remote Planning
Teledentistry enables remote consultations and treatment planning, enhancing accessibility for patients. By integrating digital tools like CBCT scans and CAD software, dentists can design surgical guides collaboratively in real-time, improving precision and streamlining the implant placement process. This approach reduces the need for in-person visits, making dental care more convenient and efficient for both clinicians and patients globally.
Challenges and Limitations
High costs, limited accessibility, and the need for specialized training hinder widespread adoption. Patient-specific anatomical variations further complicate guide customization, requiring precise adjustments for optimal results.
Cost and Accessibility Issues
The high cost of advanced dental surgical guides limits accessibility for many clinics and patients. Smaller practices often struggle to afford sophisticated systems, while patients in remote areas face limited availability of specialized professionals, exacerbating disparities in dental care quality and affordability globally.
Learning Curve for Clinicians
The adoption of advanced dental surgical guides requires significant training and practice for clinicians. Mastering digital design software and understanding complex anatomical data can be challenging, especially for those unfamiliar with modern technologies. This steep learning curve may delay integration into routine practice, potentially affecting the efficiency of surgical procedures and patient care initially.
Patient-Specific Anatomical Variations
Patient-specific anatomical variations pose significant challenges in dental surgical guide design. Each individual’s unique jaw structure, bone density, and surrounding tissue require highly customized guides. Even minor anatomical differences can affect the fit and accuracy of the guide, necessitating precise planning and adaptation. Advanced imaging and software help address these variations, ensuring optimal surgical outcomes tailored to each patient’s needs.
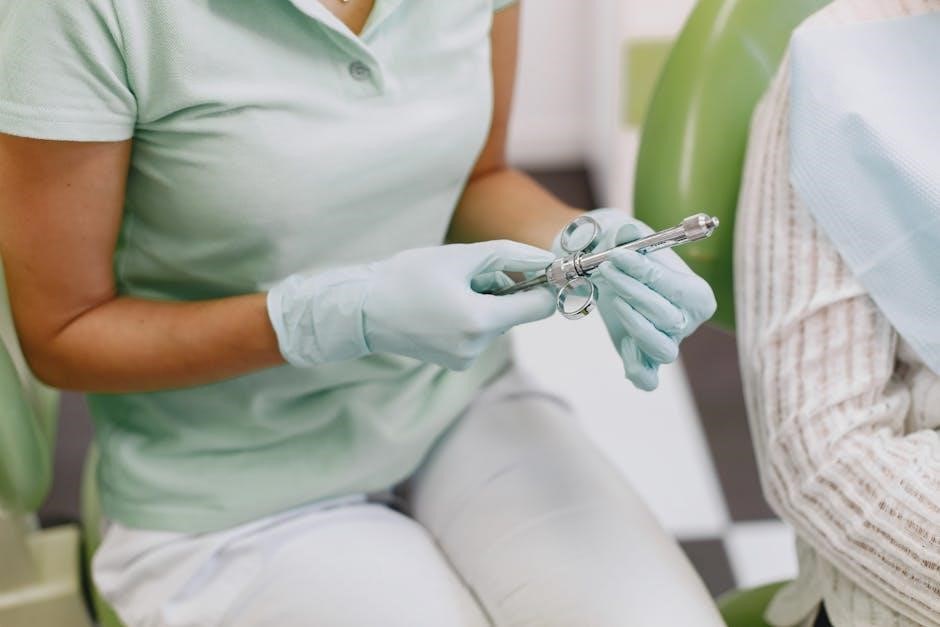

Best Practices for Dentists
Adhering to best practices ensures optimal use of dental surgical guides. Thorough pre-surgical planning, precise guide fabrication, and clear patient communication are essential for successful outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Pre-Surgical Planning and Patient Consultation
Accurate diagnosis and treatment planning are crucial. CBCT scans provide detailed 3D visualization, enabling precise guide design. Patient consultation ensures understanding of the procedure, expected outcomes, and risks, fostering trust and informed decisions.
Intraoperative Use of Surgical Guides
Surgical guides ensure precise implant placement during surgery. They are securely stabilized, often using adjacent teeth or mucosal support, to guide drill placement. This tool enhances accuracy, minimizing deviations and complications. Different guide types, such as tooth- or bone-borne, are selected based on patient anatomy. Their use streamlines the procedure, reducing surgical time and improving outcomes, while maintaining patient comfort and promoting faster healing.
Post-Surgical Care and Follow-Up
After implant placement, patients must follow specific care instructions to ensure proper healing. This includes monitoring swelling, managing discomfort with prescribed medication, and maintaining oral hygiene. A soft food diet is recommended to avoid disturbing the implant site. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to assess healing progress and remove temporary restorations. Proper post-surgical care minimizes complications and supports long-term implant success.